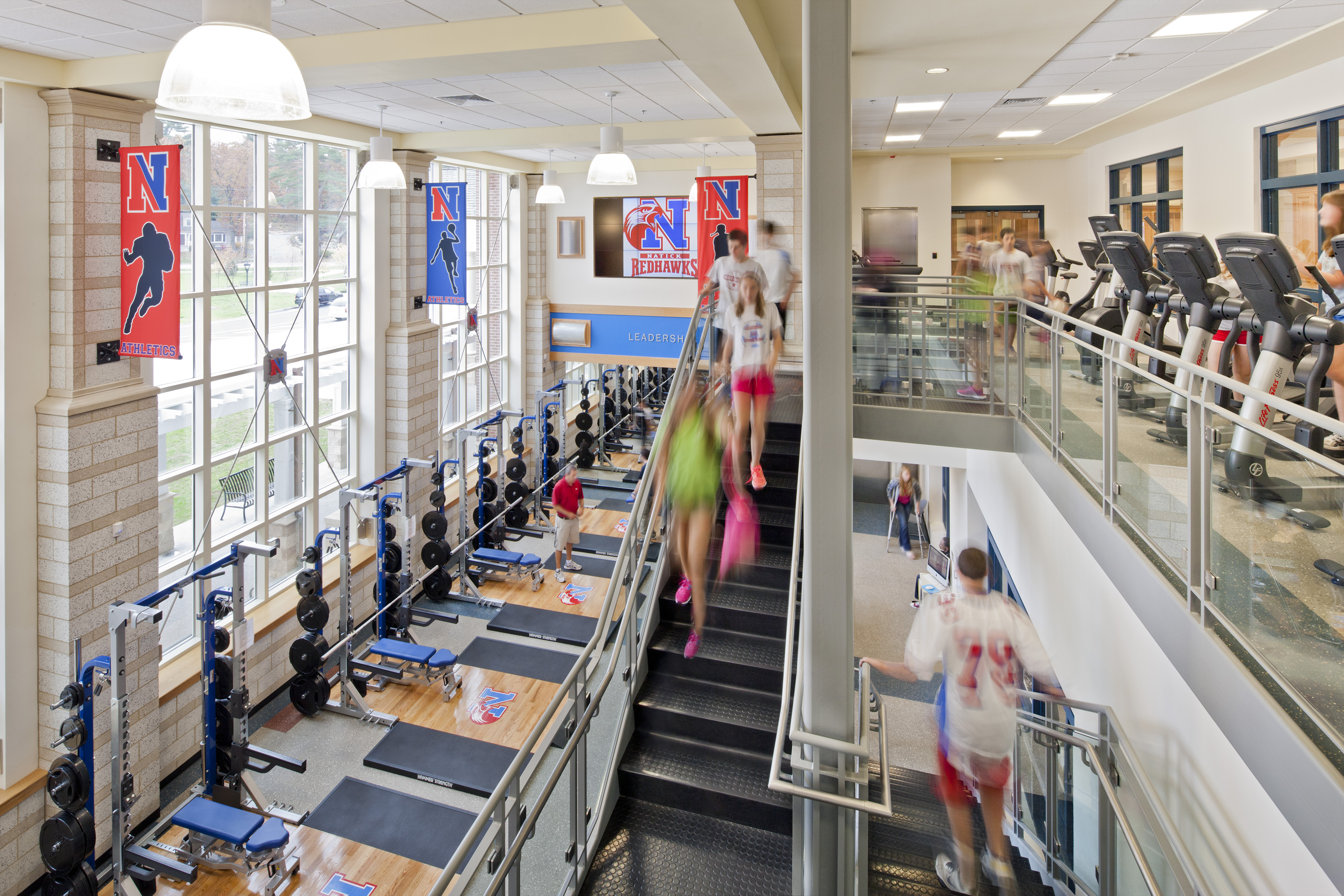
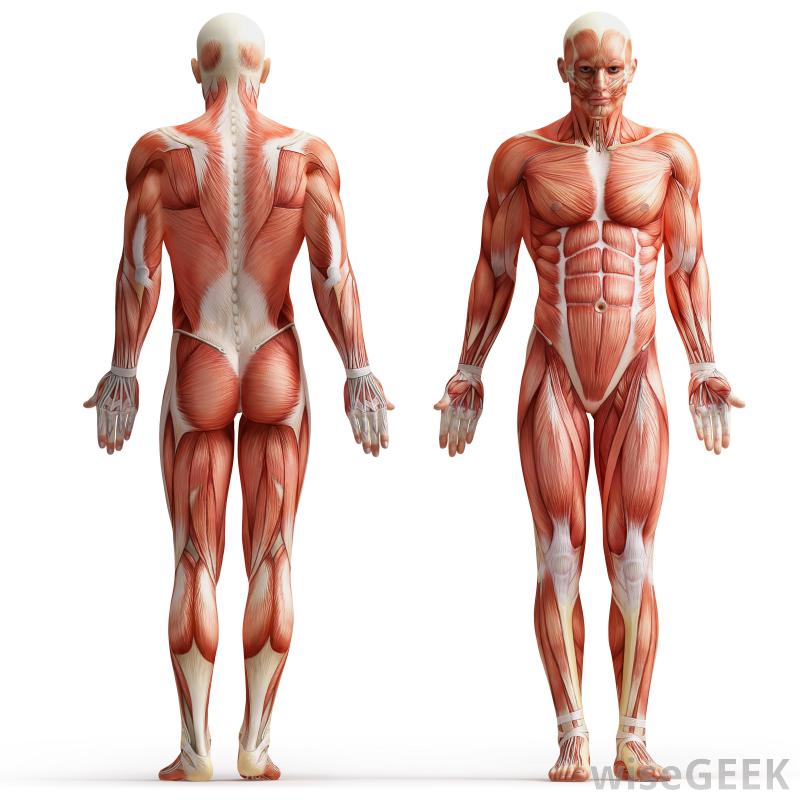
Muscles
There are three types of muscles: skeletal- biceps, triceps, quadriceps; cardiac- heart; and smooth-digestive system and other involuntary muscle tissue. Muscles are classified by shape, size, latin name, origin or insertion (location), and action.
There are also two types of muscle fibers: fast-twitch and slow-twitch. There are many types of muscles, here are a few examples:
Click the links above to learn more!
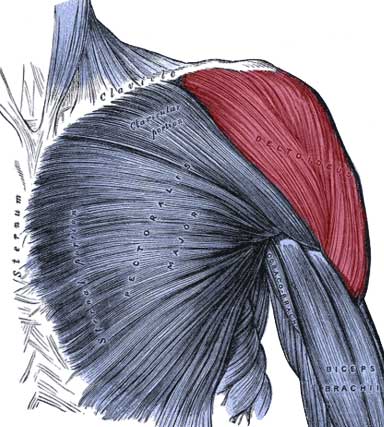
Muscles
Deltoids
Forms the rounded contour of the shoulder. There are three parts: the front portion, the middle portion, and the posterior portion. The middle portion abducts the arm at the shoulder, and the posterior portion laterally rotates and extends the arm at the shoulder.
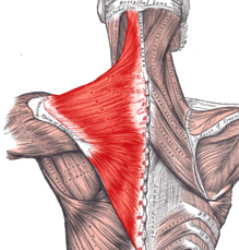
Trapezius
The trapezius is a large superficial muscle on the back that vontrols shrugging the shoulders up and down, and drawing the shoulder blades together. The strain on trapezius is often the cause of lower neck pain.
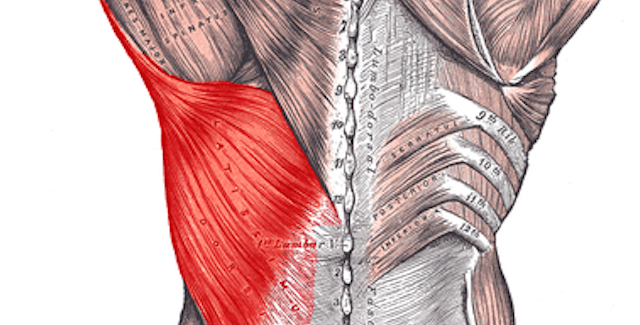
Latissimus Dorsi
The lats are triangular shaped muscles that covers the lumbar part of the back.
or go to
Muscles
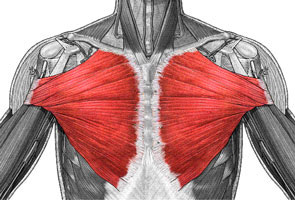
Pectoralis
The pectoralis is a thick muscle that covers the anterior (upper front) part of the chest.
Biceps
This muscle located on the upper arm. It is tri-articulate, meaning that it works across three joints: the shoulder joint, elbow joint, and proximinal-radioulnar joint.
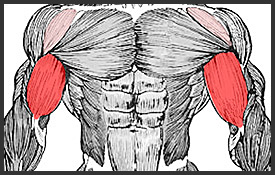
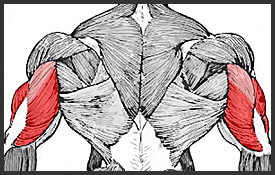
Triceps
The tricep is a large muscle that runs along the back of the upper arm. It is an extensor muscle (opens at a joint) and works in coordination with the biceps which are flexor muscles (bends at a joint).
or go to or
Muscles
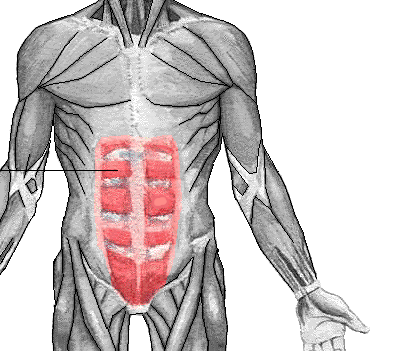
Rectus Abdominis
The rectus abdominis extends from front of the ribs to front of the pelvis. It's main job is to flex the spine forward and is well known as "6-pack abs" which comes from a very strong rectus abdominus
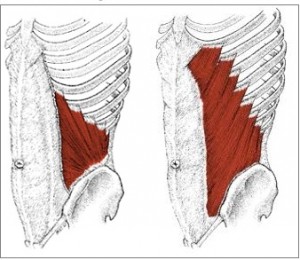
External Obliques
There are three of them on each side of the rectus abdominus. They allow the trunk to twist, but to the opposite side that the muscle contracts (unique characteristic of that group of muscles). It assists with exhalation and supports the organs inside the body cavity.
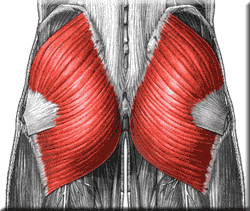
Gluteus Maximus
The gluteus maximus makes up shape and appearance of the buttocks. It also maintains the trunk in the erect posture.
or go to or
Muscles
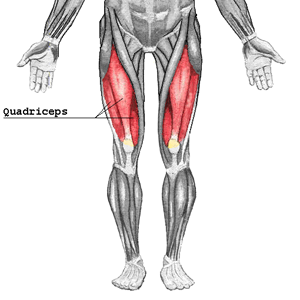
Quadriceps
The quads include the four major muscles on the front of the thigh (quad=4). It is the extensor muscle (muscle that opens a joint) of the knee. It is crucial for walking, running, squatting, and jumping.
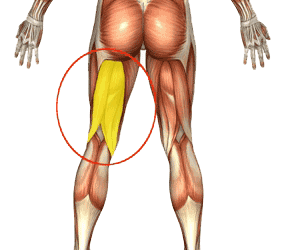
Hamstring
The hamstrings begin just underneath the gluteus maximus and attach to the tibia. The primary function is knee flexion (bringing the heel towards the buttocks). When exercised without being stretched, hamstring injuries (strains, pulls, etc.) are very common.
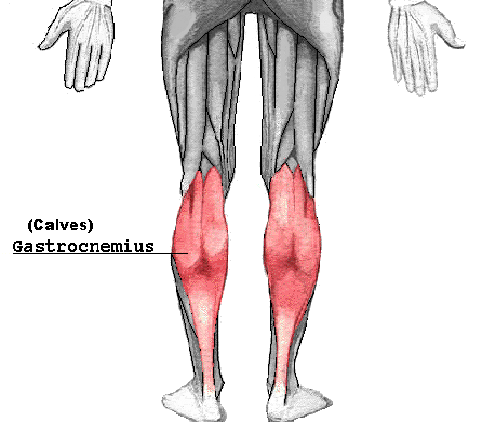
Calves
The calves are the muscles at the bottom of the leg. Their function is to stabilize during walking, running, and jumping.
or go to